Understanding the Two Sum Problem
Hey everyone! Today, I want to talk to you about a classic problem called the Two Sum problem. It's a great exercise for beginners, and it might just pop up in coding interviews too! The problem itself is pretty simple, but it can lead us to some interesting solutions. Let's dive in!
The Problem Statement
So, here’s what the Two Sum problem is all about: Given an array of integers and a target integer, we need to find two numbers in that array that add up to the target. If we find such a pair, we’ll return their indices. If we can’t find them, we’ll just return an empty array.
Example
Let’s make this clearer with an example. Imagine we have the following array:
arr = [2, 7, 11, 15]
target = 9
In this case, the numbers 2 and 7 add up to 9. Their indices are 0 and 1. So, we would return:
[0, 1]
Brute-Force Approach
Now, let’s talk about the first way to solve this problem—the brute-force approach. This method is straightforward, but it’s not the most efficient.
Steps
Here’s how the brute-force solution works:
- We loop through each element in the array.
- For each element, we loop through the remaining elements.
- We check if the sum of the two elements equals the target.
Java Code
Let me show you how we can implement this in Java:
public class TwoSumBruteForce {
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[] {i, j};
}
}
}
return new int[] {}; // Return an empty array if no solution is found
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int target = 9;
int[] result = twoSum(nums, target);
System.out.println("Indices: " + result[0] + ", " + result[1]);
}
}
Time and Space Complexity
Now, let's break down the complexity of this brute-force approach:
- Time Complexity: O(n²). This is because we have two nested loops that each go through the array.
- Space Complexity: O(1). We’re not using any additional data structures here.
Optimized Approach
Next up, let’s explore a more efficient method—the optimized approach. This one uses a hash map to keep track of the numbers we've already seen and their indices, which allows us to find the solution more quickly.
Steps
Here’s how the optimized approach works:
- We create a Hash Map to store numbers and their corresponding indices.
- We loop through the array.
- For each number, we calculate its complement (which is the target minus the current number).
- We check if this complement exists in the hash map.
- If it does, we return the indices; if not, we add the current number to the hash map.
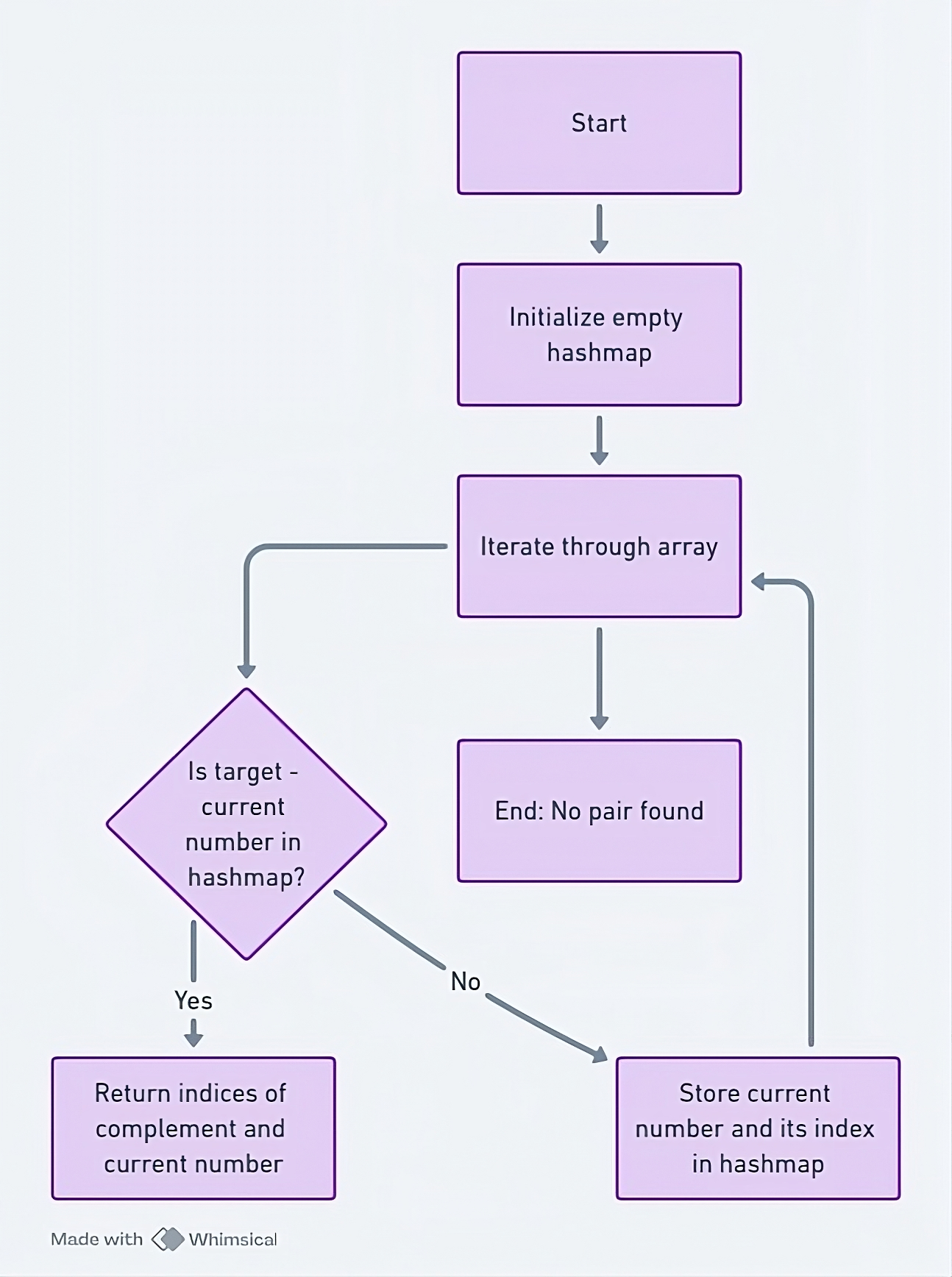
Flow Chart
Here's a flowchart explaining the optimized approach,
Java Code
Here’s how to implement the optimized solution in Java:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class TwoSumOptimized {
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(complement)) {
return new int[] {map.get(complement), i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[] {}; // Return an empty array if no solution is found
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int target = 9;
int[] result = twoSum(nums, target);
System.out.println("Indices: " + result[0] + ", " + result[1]);
}
}
Time and Space Complexity
Now, let’s analyze the complexity of this optimized approach:
- Time Complexity: O(n). We only loop through the array once, which makes this method much faster for larger datasets.
- Space Complexity: O(n). We store the elements in the hash map.
Conclusion
And there you have it! The Two Sum problem is a fantastic exercise to sharpen your coding skills. We explored both the brute-force and optimized approaches to solve it in Java. The brute-force method is easy to grasp, but the optimized approach is way more efficient, especially as the size of the array grows.
I encourage you to try out the code and play around with different inputs—it's a great way to solidify your understanding! If you have any questions, thoughts, or just want to share your experience, feel free to reach out to me on LinkedIn or drop me an email using the contact information in the footer.